On this occasion I share information on how to repair the registry Windows XP
This article describes how to recover a Windows XP that will not start because the registry is damaged. This procedure does not guarantee full recovery of the system to its previous state, but to use it should be possible to recover the data. In Windows XP it is possible to recover a corrupted registry. Corrupted registry files produce different error messages. See Knowledge Base articles about error messages related to registry issues. In this article assumes that normal recovery methods have not solved the problem and you can only access the system using the Recovery Console. If there is a backup Automated System Recovery (ASR Automatic System Recovery) is the best option for recovery, it is recommended that you use the ASR backup before attempting the procedure described in this article. Note: Make sure replace all five registry hives. If you only replace one or two sections, can cause potential issues because software and hardware may have settings in multiple locations in the registry. When you start or restart a Windows XP-based computer, you may receive one of the following error messages:
Can not start Windows XP because the following file is corrupted or missing: \ WINDOWS \ SYSTEM32 \ CONFIG \ SYSTEM Can not start Windows XP because the following file is corrupted or missing: \ WINDOWS \ SYSTEM32 \ CONFIG \ SOFTWARE Stop: c0000218 {Registry File Failure} The registry can not load the hive (file): \ SystemRoot \ System32 \ Config \ SOFTWARE or its log or alternate The procedure described in this article uses Recovery Console (System Restore ) and indicate the steps in order to ensure that the process is completed correctly. Once this procedure, the system should return to a state very similar to that in which it was before the problem occurred. If you have ever run NTBackup and completed a system state recovery, not to follow the procedures in parts two and three; can go to part four. Part One In this part, start the Recovery Console, create a folder temporary, will back up the existing registry files to a new location, delete the registry files at their current location, and then copy the registry files from folder to folder recovery System32 \ Config. A After completing this procedure, you create a registry that can be used to restart Windows XP. This registry was created and saved during the initial installation of Windows XP, so you lose any changes and settings made after installation. To complete part one, follow these steps: Start the Recovery Console. At the command prompt Recovery Console, type the following lines, pressing ENTER after each: md tmp copy c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ system c: \ windows \ tmp \ system.bak copy c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ software c: \ windows \ tmp \ software.bak copy c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ sam c: \ windows \ tmp \ sam.bak copy c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ security c: \ windows \ tmp \ security.bak copy c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ default c: \ windows \ tmp \ default.bak delete c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ system delete c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ software delete c : \ windows \ system32 \ config \ sam delete c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ security delete c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ default copy c: \ windows \ repair \ system c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ system copy c: \ windows \ repair \ software c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ software copy c: \ windows \ repair \ sam c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ sam copy c: \ windows \ repair \ security c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ security copy c: \ windows \ repair \ default c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ default Type exit to exit Recovery Console. The computer restarts. Note: This procedure assumes that Windows XP is installed in the folder C: \ Windows. If you are in a different location, be sure to change C: \ Windows to the appropriate Windows folder. If you have access to another computer, to save time copy the text in step two, and then create a text file called, for example, Regcopy1.txt. To create this file, run the following command to start the computer in Recovery Console: batch Regcopy1.txt batch command in Recovery Console allows you to process in sequence all commands in a text file. When using the batch command is not manually type as many commands. Part two To complete the procedure described in this section, must log on as administrator or an administrative user (a user who has an account in the Administrators group). If you use Windows XP Home Edition, you can login as root. In this case, you must start Windows XP Home Edition in Safe Mode. To start the Windows XP Home Edition in Safe Mode, follow these steps: Note: Print these instructions before proceeding. You can not view after starting the computer in Safe Mode. If you use the NTFS file system, also print the instructions in Knowledge Base article Q309531, which is referenced in step seven. Click Start-> Shutdown -> Restart -> OK. Press the F8 key. In a computer configured to start multiple operating systems, you can press F8 when the Startup menu appears. Use the arrow keys to select the appropriate Safe Mode and then press ENTER. If you have a dual boot system or multiple, use the arrow keys to select the installation that you want to access, and then press ENTER. In part two, you copy the registry files from the location where the copy was made of security using System Restore. This folder is not available in Recovery Console and is generally not visible during normal use. Before starting this procedure, you must change some settings to make the folder visible: Start Windows Explorer. On the Tools menu, click Folder Options-> View tab-> Hidden files and folders, click to select Show hidden files and folders, and then click to clear the check box Hide protected operating system files (recommended). Click Yes when the dialog box that confirms that you want to display these files. Double-click the drive letter where you installed Windows XP to get a list of folders. It is important to click the correct drive. Open the System Volume Information folder. This folder appears dimmed because it is an ultra-hidden folder. Note: This folder contains one or more _restore {GUID} folders such as _restore {87BD3667-3246-476B-923F-F86E30B3E7F8}. Note: you may see the message following error: Can not access C: \ System Volume Information. Access is denied. If you see this message, see the following Microsoft Knowledge Base for instructions to access the folder and able to continue with the procedure: 309531 How to Gain Access to the System Volume Information Folder Open a folder that has not been created at this time. You may have to click Details on the View menu to display the date and time of creation of folders. Under this folder can have one or more folders starting with "RP x. These restore points. Open a folder to locate the Snapshot subfolder, the path following is a snapshot folder location for example: C : \ System Volume Information \ _restore {-73EF-47BC D86480E3-A0EB-A81BE6EE3ED8} \ RP1 \ Snapshot Copy the following files from folder to folder Snapshot are the registry files that were backed up in System Restore. Because you used the registry file created by Setup, this registry does not know that the restore points exist and are available. It creates a new folder with a new GUID under System Volume Information and a restore point that includes a copy of the registry files copied during part one. This is because it is important not to use the most current folder, especially if the brand date and time the folder is the same as the date and time. The current configuration system does not know the previous restore points. To make the previous restore points available, you need a previous copy of the registry from a point previous restoration. The registry files that were copied to the Tmp folder subfolder C: \ Windows move to assure their availability in the recovery console. You need to use these files to replace the registry files currently stored in the folder C: \ Windows \ System32 \ Config. By default, Recovery Console does not have access to all folders and files can not copy the System Volume folder. Note: The procedure described in this section assumes that you run the FAT32 file system on your computer. Part Three In this part, you delete the existing registry files, and then you copy the registry files in the System Restore folder C: \ Windows \ System32 \ Config: Start Recovery Console. At the command prompt recovery console, type the following lines, pressing ENTER after each: del c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ sam del c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ security del c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ software del c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ default del c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ system copy c: \ windows \ tmp \ _REGISTRY_MACHINE_SOFTWARE c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ software copy c: \ windows \ tmp \ _REGISTRY_MACHINE_SYSTEM c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ system copy c: \ windows \ tmp \ _registry_machine_sam c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ sam copy c: \ windows \ tmp \ _registry_machine_security c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ security copy c: \ windows \ tmp \ _REGISTRY_USER_.DEFAULT c: \ windows \ system32 \ config \ default Note Some of the above command lines have been adjusted to make them readable. Note : This procedure assumes that Windows XP is installed in the folder C: \ Windows. If you are in a different location, be sure to change C: \ Windows to the appropriate Windows folder. If you have access to another computer, to save time copy the text in step two, and then create a text file called Regcopy1.txt, for example. Part Four Click Start-> All Programs-> Accessories -> System Tools-> System Restore and Restore my computer to an earlier time.









 Greetings to all who visit our blog Free Pc Repair section today in our computer repair we will give exact steps to follow to remove the bios password . Many will say that is that, as I explain, there are times which we have to change some parameters of the internal configuration of the PC and as you know all these settings are stored in the battery of the motherboard, this saves both information that we have hard drives installed in your PC, the computer time, how much RAM, and what kind of drives you have in total, so it has the option of setting a password, so that not anyone can access those settings and remove any fence configuration that affect the performance of your PC, and Since we know the key changes we have to remove to access the PC setup. Now the steps to remove the password of the bios are
Greetings to all who visit our blog Free Pc Repair section today in our computer repair we will give exact steps to follow to remove the bios password . Many will say that is that, as I explain, there are times which we have to change some parameters of the internal configuration of the PC and as you know all these settings are stored in the battery of the motherboard, this saves both information that we have hard drives installed in your PC, the computer time, how much RAM, and what kind of drives you have in total, so it has the option of setting a password, so that not anyone can access those settings and remove any fence configuration that affect the performance of your PC, and Since we know the key changes we have to remove to access the PC setup. Now the steps to remove the password of the bios are
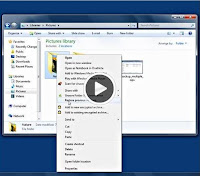 Hello to all who visit this website today teach them how to recover deleted files on Windows 7 sometimes happens that we're working on our pc and suddenly inadvertently deleted some files and want to recover, Windows 7 comes with a function that allows us to recover deleted files, to do so we must do the following: Recovering Deleted Files In Windows 7 1. Click the Start button and then click Computer. 2. Navigate to the folder containing the file or folder, right click it with the right mouse button and then click Restore previous versions. If the folder was in the top level of a unit, for example C: \, click the right mouse button on the drive and then click Restore previous versions. A list of available versions of the file or the folder. The list will include both files saved on a backup (if you use Windows Backup to back up your files) and restore points, if both types are available.
Hello to all who visit this website today teach them how to recover deleted files on Windows 7 sometimes happens that we're working on our pc and suddenly inadvertently deleted some files and want to recover, Windows 7 comes with a function that allows us to recover deleted files, to do so we must do the following: Recovering Deleted Files In Windows 7 1. Click the Start button and then click Computer. 2. Navigate to the folder containing the file or folder, right click it with the right mouse button and then click Restore previous versions. If the folder was in the top level of a unit, for example C: \, click the right mouse button on the drive and then click Restore previous versions. A list of available versions of the file or the folder. The list will include both files saved on a backup (if you use Windows Backup to back up your files) and restore points, if both types are available. Many are wondering how to clean ram memory on my pc , well then today it will teach how to clean your PC memory ram , often accumulated dirt inside your PC may be the reason why your PC is giving you a malfunction . often happens that we feel that our computer is very slow, programs do not load faster we can all be caused by dust or dirt inside the PC, and sometimes when RAM is dirty it can generate a problem, so today I will give you the steps to clean the PC's RAM . The steps to clear the RAM of the PC are: 1. We must first verify that your PC is completely off, there must be connected to energy. 2. Touch a metal part of the PC to remove any static to prevent damage to your PC, or for security use a static wristband connected to a metal part of the computer. 3. Open the cabinet of the PC and verify the location of RAM you can see each memory module is subject to the slot with a white levers have to push them both out to free memory slot. 4. With an electronic contact cleaner , apply a small portion in the contacts and then with a piece of flannel press a little and clean for one minute, then you can see that the dirt is on the shirt.
Many are wondering how to clean ram memory on my pc , well then today it will teach how to clean your PC memory ram , often accumulated dirt inside your PC may be the reason why your PC is giving you a malfunction . often happens that we feel that our computer is very slow, programs do not load faster we can all be caused by dust or dirt inside the PC, and sometimes when RAM is dirty it can generate a problem, so today I will give you the steps to clean the PC's RAM . The steps to clear the RAM of the PC are: 1. We must first verify that your PC is completely off, there must be connected to energy. 2. Touch a metal part of the PC to remove any static to prevent damage to your PC, or for security use a static wristband connected to a metal part of the computer. 3. Open the cabinet of the PC and verify the location of RAM you can see each memory module is subject to the slot with a white levers have to push them both out to free memory slot. 4. With an electronic contact cleaner , apply a small portion in the contacts and then with a piece of flannel press a little and clean for one minute, then you can see that the dirt is on the shirt. Greetings to all who visit our web site computer repair this time I'll show you how to clean the PC's motherboard or rather known as motherboard , as we all know cleaning your PC has a great importance to so can be in perfect condition that is why cleaning the motherboard is very important. But if we are users who live in areas where dust moves a lot, that's why it is necessary always to give a cleaning our motherboard to we are not many problem, then tell them the steps on how to clean the motherboard of your PC . 1. The first point we have to remove any static by touching the metal part of your PC to prevent damage to the circuitry of the PC. 2. Open the cabinet of your PC to discover the Motherboard. 3. With a small brush about 3 centimeters in width removes dust 4. Once you have removed the dust or at least have taken off "torch" with an air compressor or a can of compressed air. 5. If you've used the compressor then I recommend you give it a pass with a hair dryer because sometimes release water. 5. Optionally, once your motherboard is free of dust can give a Pasadita with used oil for sewing machines.
Greetings to all who visit our web site computer repair this time I'll show you how to clean the PC's motherboard or rather known as motherboard , as we all know cleaning your PC has a great importance to so can be in perfect condition that is why cleaning the motherboard is very important. But if we are users who live in areas where dust moves a lot, that's why it is necessary always to give a cleaning our motherboard to we are not many problem, then tell them the steps on how to clean the motherboard of your PC . 1. The first point we have to remove any static by touching the metal part of your PC to prevent damage to the circuitry of the PC. 2. Open the cabinet of your PC to discover the Motherboard. 3. With a small brush about 3 centimeters in width removes dust 4. Once you have removed the dust or at least have taken off "torch" with an air compressor or a can of compressed air. 5. If you've used the compressor then I recommend you give it a pass with a hair dryer because sometimes release water. 5. Optionally, once your motherboard is free of dust can give a Pasadita with used oil for sewing machines.